Home / Success Stories / Saving water with smart management and efficient systems in Spain
Do you want this case study in pdf?
Download it in English🇬🇧 and Spanish🇪🇸 directly to your inbox.
DownloadWater and electrical supply are two of the main concerns for public authorities. The demand of these resources grow as fast as the population in urban areas so they would become scarcer with the pass of the years. A Technavio report states that the use of smart water management technologies such as Big Data, sensoring and monitoring in real-time can help save more than USD 12 billion revenues for utilities annually.
Madrid (Spain)
Some of the areas where IoT developments can improve smart water infrastructures are drainage or water supply plans, leakage detection services, network performance optimization and GIS management. The project called iWesla, which stands for Improving Water Efficiency and Safety in Living Areas, is a CPSE Labs funded by the European Union´s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. The consortium is formed by A-CING, Indra, Novelti and the Universidad Politecnica de Madrid (UPM).
The wireless sensor networks developed in iWesla are based on Waspmote Sensor Platform. A-CING (Aqua-Consult Ingenieros), a consulting and engineering company specialized in water management projects and ICT-based environmental solutions using wireless communications trusted the Sensor Platform due to its modularity and scalability.
Living area water efficiency and safety solution
The solution prototype was tested in UPM Campus Sur with the premise to be scaled up and deployed in two pilot sites provided by the Municipality of Rivas Vaciamadrid (Madrid, Spain), a primary school and a sports center, to enhance the impact on the citizens.
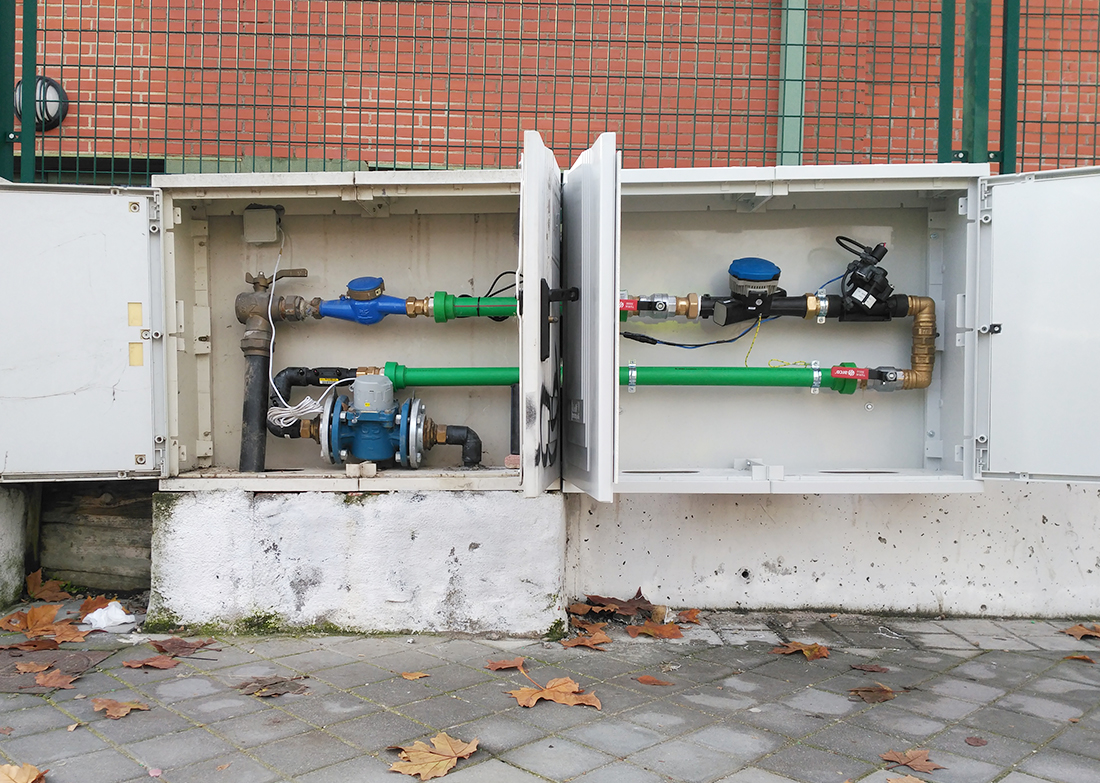

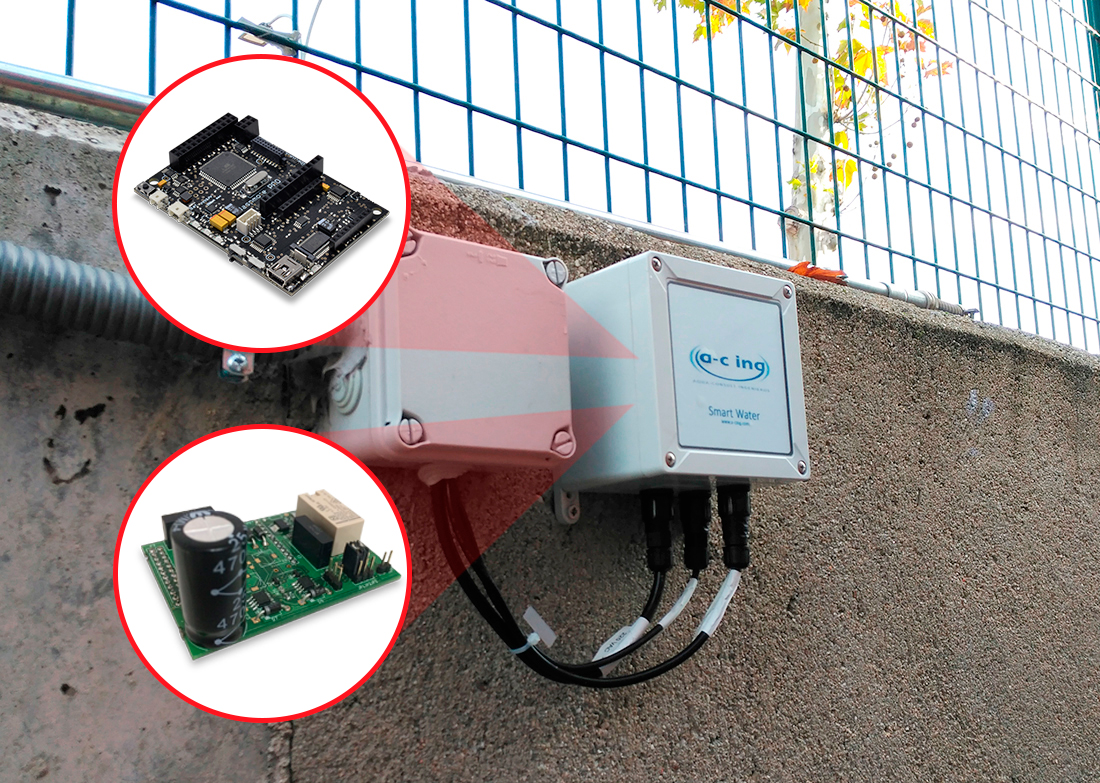
Smart water management system developed in a primary school in Madrid
The smart water project aims to develop and deploy a demand-side cyber-physical system (CPS) to optimize the water consumption efficiency and safety in living areas. The system consists of:
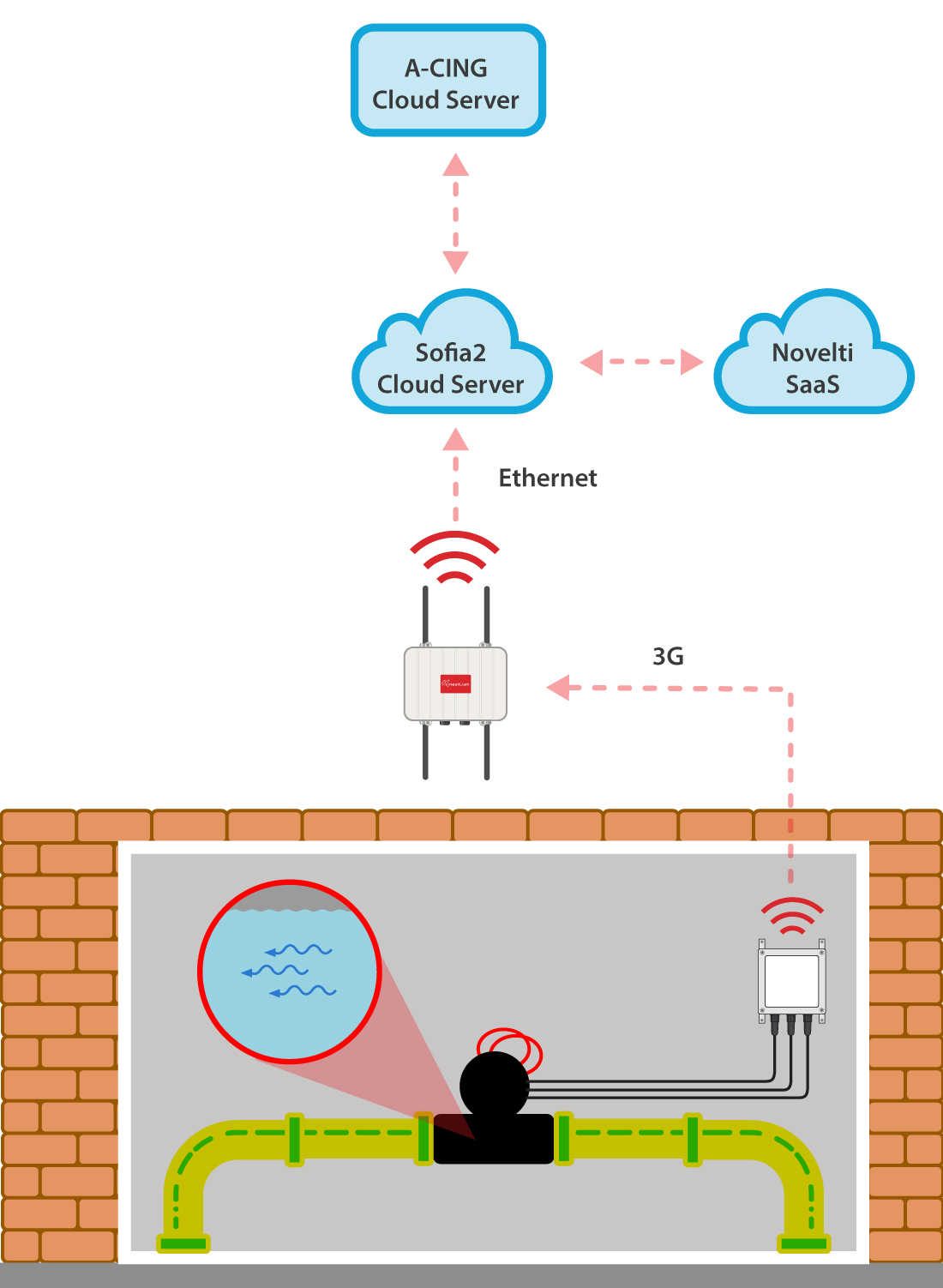
Diagram of iWesla deployment
The communication between the sensor platforms and Meshlium is carried out through 3G communications. The IoT Gateway collects data and sends it to the FEEP IoT & Big Data Platform Sofia2 through Ethernet connection. Novelti analytic service processes the water consumption information gathered by FEEP IoT & Big Data Platform Sofia2 based Application, returning the disaggregated water usage made by all consumption points in the living area. The processed information is visualized in a Web Application designed and developed by A-CING.
Cutting down costs near 50%
The water efficiency and safety solution designed in iWesla could help saving up to 50% of the water consumption in living areas thanks to the detection of abnormal water consumption. When detected, the user is warned using alarms and given the possibility to actuate over the electric valve to close the water flow. Apart from the reduction in the water consumption, this early detection can lead to the reduction of potential damages caused by leakages or open taps.
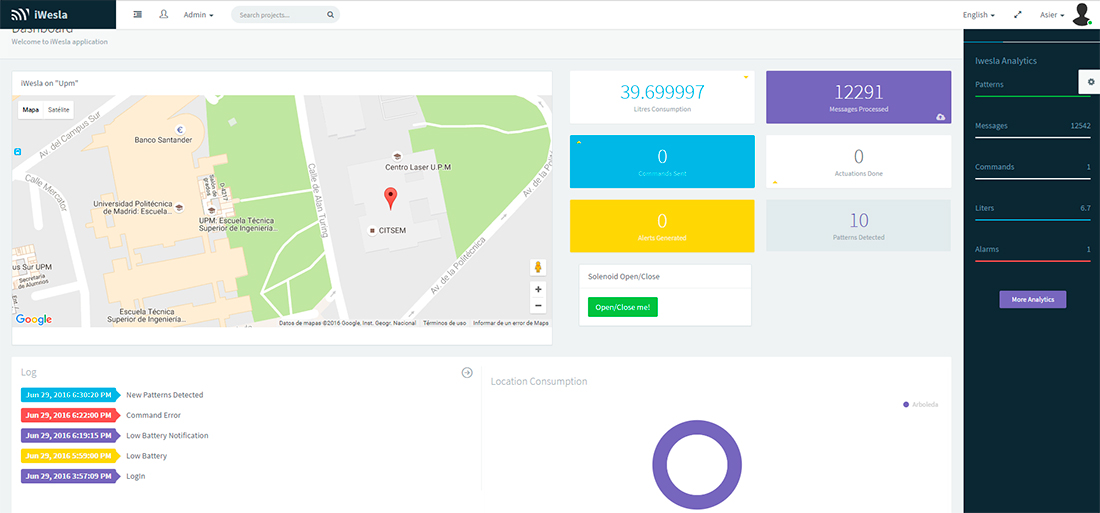
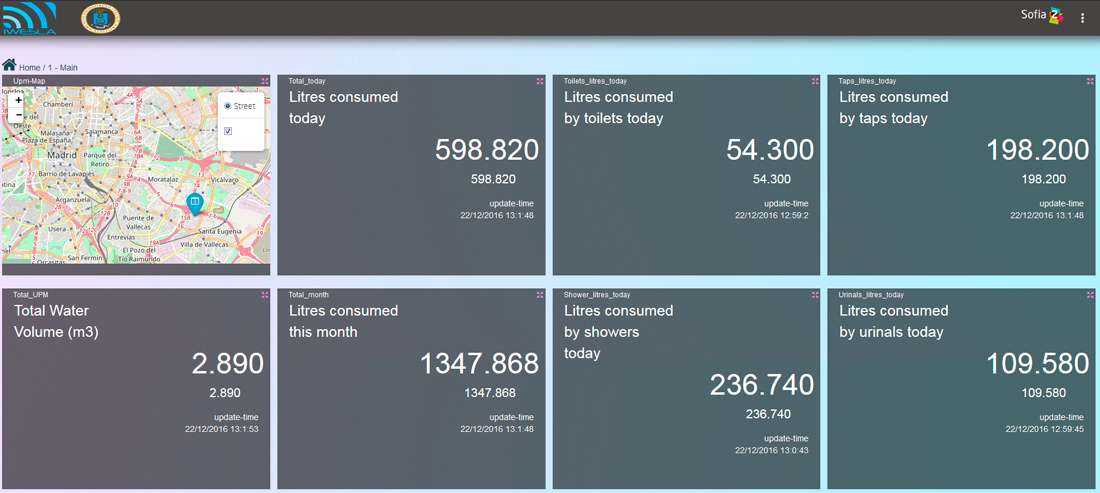
iWesla dashboard to visualize data
One of the main challenges faced during the system development was the disaggregation of the water consumption actions using the data gathered from the main water supply pipe, such as number of times people pull the chain, take a shower, open the water tap or turn on the dishwasher. Apart from the system management web front-end, a consumption awareness application has been developed to allow users to be informed about the water consumption habits, raising awareness and leading to a responsible consumption, creating an impact on the citizen’s water consumption patterns.
FEEP IoT & Big Data Platform Sofia2
Deploying wireless sensors networks to achieve smart management in infrastructures is one of the most important goals for public authorities and large water consumers. The optimization of water use and also the water supply network performance allow cutting down resources waste and also the water bill for organizations.

Public primary school where iWesla project has been deployed
The current rate of growth of the population in cities together with climate change effects requires the optimization of natural resources usage. The intelligent use of water in smart cities implies engagement and involvement from the water utilities to the demand side or end-users such as citizens, municipalities or building management staff.
For more information about our products contact the Libelium Sales Department.
If you want to download the article in Spanish, please click here.
More info:
References:
Download it in English🇬🇧 and Spanish🇪🇸 directly to your inbox.
DownloadStay up to date in IoT!
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest, exciting news.
More than 18 years of experience in IoT support us.


















© Libelium Comunicaciones Distribuidas S.L. | Terms And Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookies Policy | Security Policy | Reporting Channel