IoT technology to track, forecast and reduce pollution in European Cities
Libelium is involved in European project aiming to predict and reduce emissions utilising open source philosophy.
Air pollution is known as ‘the silent killer’ as it is not always visible, but it certainly can be deadly. Pollution causes 29% of lung cancer deaths, 24% of heart attack deaths, 25% of cardiovascular disease deaths and 43% of lung disease deaths, according to WHO (The World Health Organization).
Air pollution is known as the ‘silent killer’ according to WHO
The European Comision and several institutions have led the project Trafair with the aim of estimating the level of pollution on an urban scale in order to achieve one of the UN’ Sustainable Development Goals for 2030. Libelium already knows how to maximize the impact the IoT provides for a better world.
The investigative project Trafair titled “Understanding traffic flows to improve air quality” has a duration of two years (2019-2021) and is a cooperation between the Innovation and Networks Executive Agency (INEA) of the European Commission and several European partners led by the Università degli studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia: Università degli Studi di Firenze, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Comune di Modena, Regione Toscana, Concello de Santiago de Compostela, Fundación Pública Gallega Centro Tecnológico de Supercomputación de Galicia, Universidad de Zaragoza and Lepida SpA.
The first step was to choose five cities as locations due to their size and characteristics to provide data that could be scaled up to larger and more polluted cities.
The locations are as follows:
- Zaragoza (Spain) – 600,000 inhabitants
- Santiago de Compostela (Spain) – 95,000 inhabitants
- Florence (Italy) – 382,000 inhabitants
- Modena (Italy) – 185,000 inhabitants
- Pisa (Italy) – 90,000 inhabitants
Location of the project
As road traffic is one of the main causes of environmental pollution in large cities, the Trafair project focuses on developing an air quality forecasting service based on weather forecasts and road traffic flow. At Santiago de Compostela the weather forecast is provided by the Environmental Quality and Climate Change Dept. of the Regional Government (through its MeteoGalicia web server).
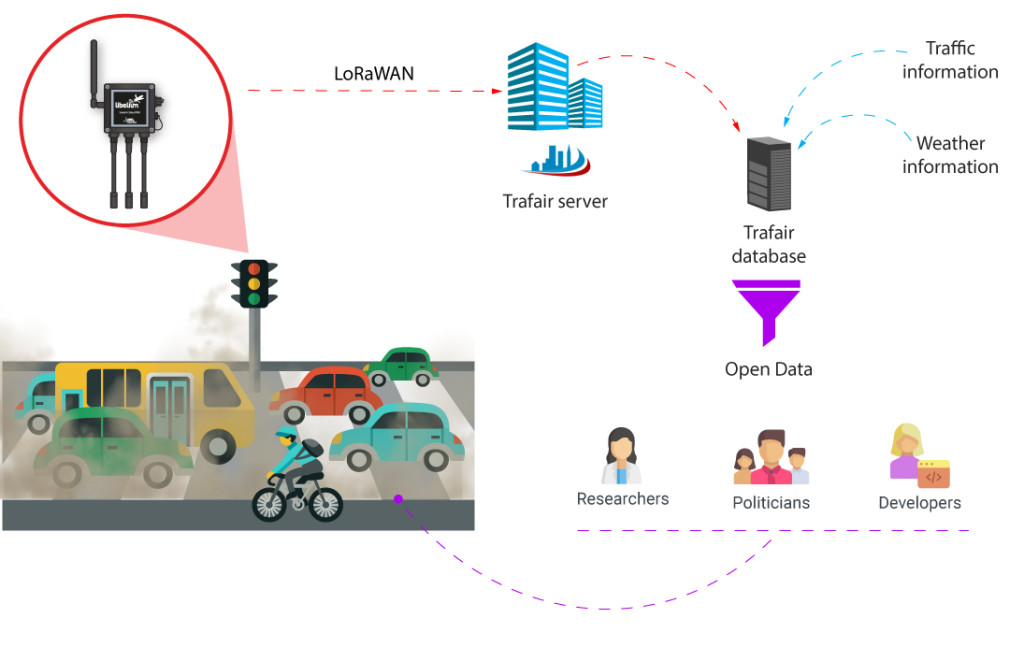
Diagram of the project
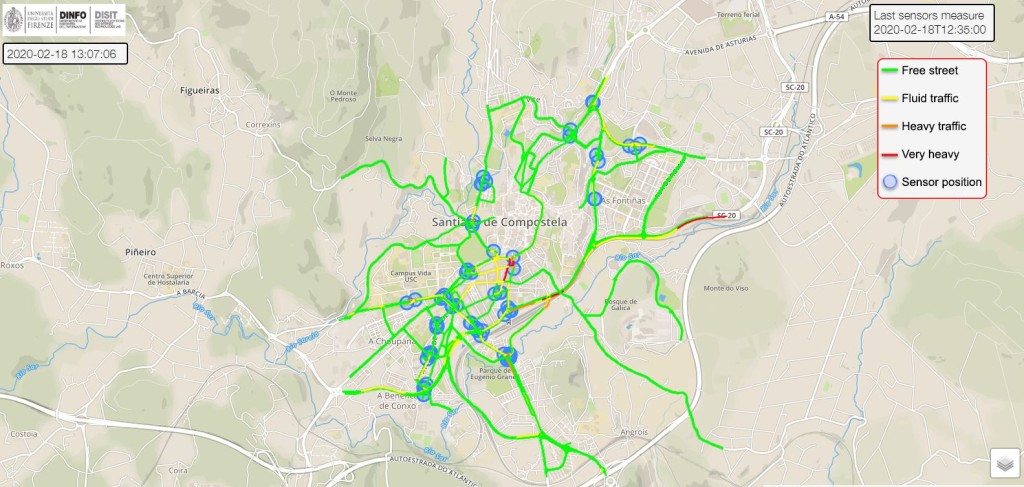
Several air quiality sensors calibrated with the reference stations have been installed in specific locations depending on the density of inhabitants, outdoor activities and especially vulnerable areas such as hospitals, schools or parks. The information is sent from the device to the Cloud through a LoRaWAN network. In Santiago de Compostela the platform installed is Libelium Smart Environment PRO Plug&Sense! with pollution detectors for measuring NO2, CO and O3 as the main road traffic related air pollutants.
Libelium Plug&Sense! Smart Environment installed in Santiago de Compostela
Each sensor is calibrated individually using the measurements of pollutant concentration as reference data provided by reference air quality stations in the city of application. At Santiago de Compostela the reference data are provided by the Environmental Quality and Climate Change Dept. of the Regional Government. After each calibration, the sensors are installed at various locations in each city to monitor air quality, with special attention to the possible influence of road traffic on air quality.
Trafair solves the challenge of receiving heterogeneous data from different devices and sensors settled by designing a data warehouse that receives the dataset and processes it to unify the measurements in order to share all data consistently. The data warehouse crosses the data with the traffic network information to design a dynamic traffic model and makes air pollution forecasts. The prediction of the air quality in the cities at street level (“street canyon”) uses Lagrangian models of forecasting of air quality executed daily on supercomputers. The dissemination of all the data generated by the air quality sensors and the models is open source for consultation and exploitation.
The air quality data is displayed in a public dasboard
Citizens and politicians must take action based on realiable data
- Developers can take this data and design web platforms, mobile apps and computer applications, designed to provide useful information to the general population.
- Public administrators can take decisions based on actual information to implement actions related to traffic management (encourage low-emission vehicles, increase public transport service, etc.) in order to reduce pollutant emissions and improve public health.
- Scientists, researchers and technicians can take the data to analyze how pollutant emissions impact in human health, food and animal life.
- Citizens can access to urban pollution data of their city with two mobile applications available for Android devices.
Libelium Plug&Sense! Smart Environtment PRO sensors are capable of providing voltage values related to the measured atmospheric parameters (concentrations of pollutants, temperature and humidity) in real time (frequency of 1-2 minutes), complying with the objectives and specifications required for the project. “As for the benefits of using Plug & Sense! units within the project, in addition to meeting the desired reliability and accuracy results, it is expected that their ease of installation and use will reduce the time spent on ensuring their operation during the project,” says José Antonio Souto González, professor and researcher at the University of Santiago de Compostela. From the university they also point out that Libelium Plug & Sense! units show a good correlation with the measurements of the same pollutants in reference stations, also demonstrating a stable response over time.
Now that we know that the Internet of Things is a great ally in the capture of reliable data, it is time to take action and take measures to curb pollution and ultimately climate change.
Want to receive this and more IoT news directly to your email?
🔔 Subscribe to our newsletter and don’t miss anything!
You will learn about IoT and how it helps to make the world a more sustainable and efficient place.
This case study helps to achieve the following Sustainable Development Goals:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Contact Libelium Sales Department for more information about our products.
More info:
- For technical details on Smart Environment PRO/Gases PRO Board Guide: Gases PRO v30 Board Guide.
- LoRaWAN technical guide
- Read more about Libelium sensor product lines in the Waspmote, Waspmote Plug & Sense! Sensor Platform and Meshlium Gateway websites.
- Drones, Sensors and Blockchain for water quality control in the Volga river to promote trustworthy data and transparency.
- Libelium releases new IoT Smart Cities Platform enhancing accuracy in noise level and air quality pollution sensors.
- New Calibrated Air Quality Sensors for Smart Cities.
References:
- Trafair Project: trafair.eu
- MeteoGalicia web server: www.meteogalicia.gal
Although this specific solution is no longer available, we now offer an evolved version that meets similar needs with improved performance and scalability.
If you’re facing a similar challenge or want to explore a customised version of this approach, contact us. We’d love to help you bring it to life.