Home / Success Stories / Detecting Radiation Levels in Fukushima: an example of crowdsourcing
 Immediately following the earthquake, the tsunami disabled the power supply and the cooling systems of three of the Fukushima Daiichi reactors, causing a nuclear accident. All three cores largely melted in the first three days, rating the accident at 7 on the INES scale, due to high radioactive releases in the first few days. Fortunately, there have been no deaths or cases of radiation sickness from the nuclear accident, but over 100,000 people had to be evacuated from their homes to ensure this.
Libelium’s response
Fukushima’s disaster also shocked Spain, and engineers at Libelium began to think about developing a new sensor board to measure radiation. Before March 2011, it was very difficult to find radiation meters on the market, and almost impossible to find one affordable for most citizens. Based on this issue, Libelium decided to develop a radiation sensor shield for the Arduino platform due to its affordability and seeming ubiquity.
In less than a month, we tested and verified a number of Geiger tubes from different manufacturers, then designed the board to connect the tube and show the radiation on a LCD screen. As a result, a series of boards were shipped at no charge to the Tokyo Hackerspace and other working groups in Japan.
The main goal of the Radiation Sensor Board for Arduino was to help people in Japan measure levels of radiation in their everyday life after the Fukushima disaster. Libelium wanted to give citizens the opportunity to monitor these levels by themselves instead of relying on local authorities. The design of the board was open hardware and the source code was released under general public license (GPL).
In addition to the Radiation Sensor Board for Arduino, Libelium launched a couple of months later the Radiation Sensor Board for Waspmote. The idea is simple, each node acts as an autonomous and wireless Geiger Counter. It measures the number of counts per minute detected by the Geiger tube and send this value using ZigBee and GPRS protocols to the control point. The system is powered with high-load internal batteries what ensures a lifetime of years.
Immediately following the earthquake, the tsunami disabled the power supply and the cooling systems of three of the Fukushima Daiichi reactors, causing a nuclear accident. All three cores largely melted in the first three days, rating the accident at 7 on the INES scale, due to high radioactive releases in the first few days. Fortunately, there have been no deaths or cases of radiation sickness from the nuclear accident, but over 100,000 people had to be evacuated from their homes to ensure this.
Libelium’s response
Fukushima’s disaster also shocked Spain, and engineers at Libelium began to think about developing a new sensor board to measure radiation. Before March 2011, it was very difficult to find radiation meters on the market, and almost impossible to find one affordable for most citizens. Based on this issue, Libelium decided to develop a radiation sensor shield for the Arduino platform due to its affordability and seeming ubiquity.
In less than a month, we tested and verified a number of Geiger tubes from different manufacturers, then designed the board to connect the tube and show the radiation on a LCD screen. As a result, a series of boards were shipped at no charge to the Tokyo Hackerspace and other working groups in Japan.
The main goal of the Radiation Sensor Board for Arduino was to help people in Japan measure levels of radiation in their everyday life after the Fukushima disaster. Libelium wanted to give citizens the opportunity to monitor these levels by themselves instead of relying on local authorities. The design of the board was open hardware and the source code was released under general public license (GPL).
In addition to the Radiation Sensor Board for Arduino, Libelium launched a couple of months later the Radiation Sensor Board for Waspmote. The idea is simple, each node acts as an autonomous and wireless Geiger Counter. It measures the number of counts per minute detected by the Geiger tube and send this value using ZigBee and GPRS protocols to the control point. The system is powered with high-load internal batteries what ensures a lifetime of years.
Fig. 2.- Waspmote & Radiation Sensor Board
With this technology radiation measurements can be known in real time without compromising the life of the security corps members as they do not have to be inside the security perimeter in order to activate the Geiger counters. The information is extracted automatically and sent wirelessly to the Gateway of the network. Waspmote has a cyclic behaviour. It sleeps most of the time in order to save battery. At specific intervals it wakes up and during 1 minute reads the pulses which are being generated in the Geiger tube calculating the counts per minute. Then it compares this value with the alarm thresholds already predefined. If normal values are found they are sent using the ZigBee radio to Meshlium, the Gateway of the network and the values stored in an Internet data base.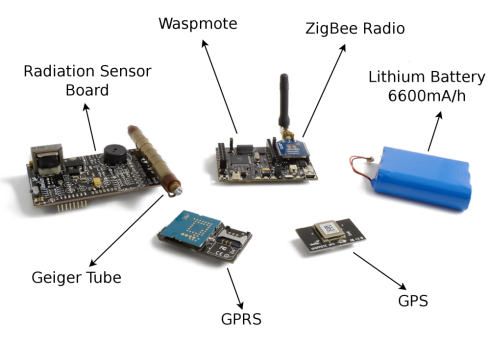
Fig. 3.- Different parts of the system for measuring Radiation using Waspmote
If the values are above the security threshold defined, as well as being sent through the ZigBee network they are also directly transmitted to the security corps by an SMS alarmwith the GPRS radio or event directly sent to the Internet via a TCP/IP socket. Along with the value extracted from the Geiger counter, Waspmote adds also the GPS information (latitude, longitude) in order to give the exact location of the radiation source. Moreover, Libelium launched recently the Waspmote Plug&Sense! Radiation Control. This new encapsulated line allows to measure the radiation as is explained above, but increasing the possibilities thanks to a great enclosure.
Fig. 4.- Waspmote Plug&Sense Radiation Control
Crowd data sharing Governments were once the only source of information regarding radiation levels around a nuclear plant or a specific zone within a country. But thanks to a cutting-edge combination of cheap radiation sensors (such as Libelium’s Radiation Sensor Board), crowdfunding and crowd data sharing, some organizations have arisen to share this kind of information with everybody. A perfect example is Safecast, a global sensor network for collecting and sharing radiation measurement founded by a small group of people in the U.S. and Japan a couple of days after the Fukushima disaster. They got money from a crowdfunding site and found some allies on the ground at the Keio University in Japan. In just four days, the project was funded by anonymous donors and started to deploy sensors in Japan and show the data on a website. Safecast’s founders proposed equipping as many people as possible in Japan with inexpensive radiation sensors. Volunteers would send in their findings over the Internet, which would then be displayed as data points on a Google map. The entire project would be open-sourced, and all the data would be made available to anyone who wanted to use it. Thanks to this initiative, anyone may contribute to gathering data related to a wide range of public health hazards where governments and industry have previously held a near-monopoly on measuring the dangers to public health. Crowd data sharing, crowdsourcing, crowdfunding and different approaches to this methodology are starting to create a new scenario where all of us can create a better and safer world. If you are interested in Waspmote, we will be glad to help you to design your system. You can request for a quotation of Waspmote here. Discover our IoT Kits at The IoT Marketplace!The IoT Marketplace
Buy off-the-shelf IoT kits