Do you prefer this case study in pdf?
Here you have it!
Location of Alaska (United States of America)
These animals have strict seasonal behavioral patterns, staying in the open ocean during the winter and migrating to warmer zones in the summer. They remain close to the continent in estuaries and shallow waters, sometimes even traveling up rivers several kilometers. On the one hand, staying in estuaries and rivers gives the animal refuge and a metabolic stimulus which facilitates the seasonal renovation of the epidermal layer. On the other hand, the environmental and acoustic pollution generated by human activities represent a real danger to these animals. Polluted substances have an adverse effect on the animals: incremental cases of cancer, reproductive pathologies and deteriorated immune system. It has been proven that, in determined areas, cancer frequency is higher and experts believe that this condition could be directly related to polluted environments. In 1972, the United States Congress enacted the Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA), in which hunting, killing, capture, and/or harassment of any marine mammal is prohibited in US waters. Nevertheless, pollution and human activities are still seriously damaging this species situation. On February 2017, a natural gas leak was detected approximately 6 kilometers offshore in the Cook Inlet near Nikiski (Alaska). The leak was immediately reported to the Alaskan authorities, which responded with detailed and challenging monitoring requirements due to the area being a critical habitat for endangered beluga whales. Libelium’s partner company Aridea Solutions (West Virginia) was tasked with designing a solution to monitor the leak. Aridea develops monitoring technology for environmental challenges. The team at Aridea Solutions, envision a time when environmental parameters are continuously monitored in real-time and can be communicated with each other, machines and people will help deliver better outcomes for our industries and the environment in which we live.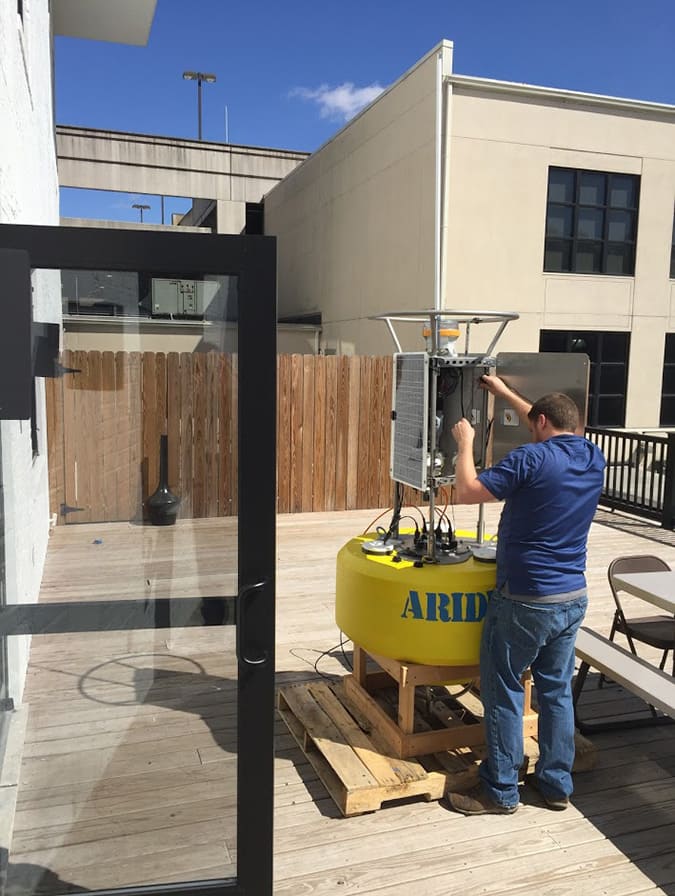
Mounting of the buoy at Aridea’s headquarters in West Virginia
After several intense hours of researching options the Aridea team devised that a buoy would be the best platform for this application. The buoy required sensors from four separate sensor manufacturers. Aridea turned to Libelium to provide the Plug & Sense! platform to allow the interfacing of various industrial protocols required to interface the sensors. The Plug & Sense! also allowed for easy aggregation and transmission of data to a ship that could be several miles away from the buoy, using a 900MHz communication protocol. Aridea designed a buoy equipped with Libelium’s wireless sensor platform to monitor air and water near the leak affecting the Beluga whales and other aquatic mammals. This project consisted of monitoring methane, oxygen and CO2 levels above the surface of the water. While simultaneously monitoring dissolved methane, dissolved O2 and several other parameters directly beneath the surface of the water.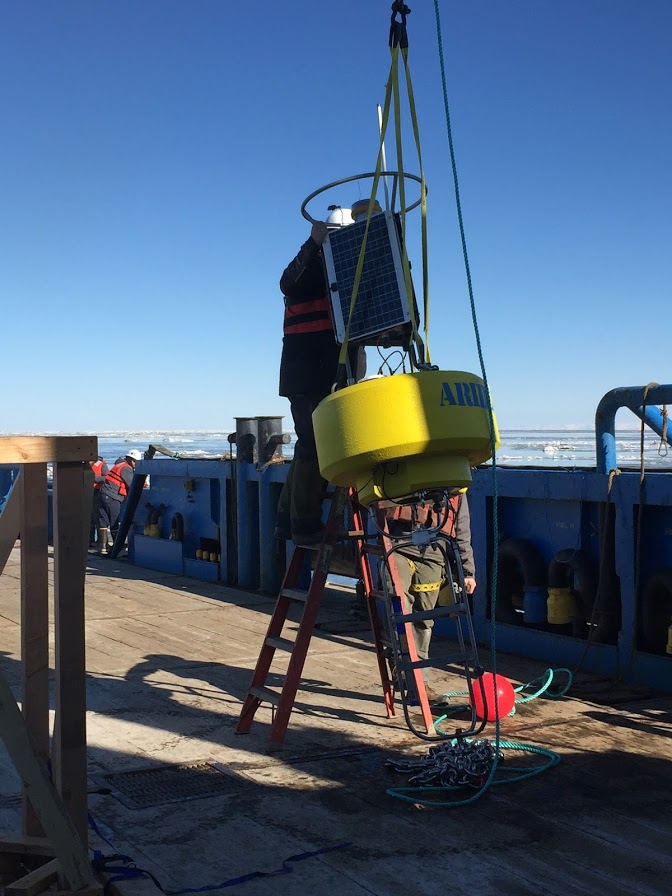
Installation of the buoy at Cook Inlet (Alaska)
The project was on a very tight timeline so Aridea engineers worked diligently for 2 weeks to design, build, and ship the buoy-based monitoring platform to the affected site in Alaska. Once on-site two Aridea engineers accompanied the buoy to help with deployment, training, and sensor calibration. The buoy performed as designed and returned key data for scientists to analyze and quickly help quantify the overall environmental impact.| Measured parameters in the air | Measured parameters in water |
|
|
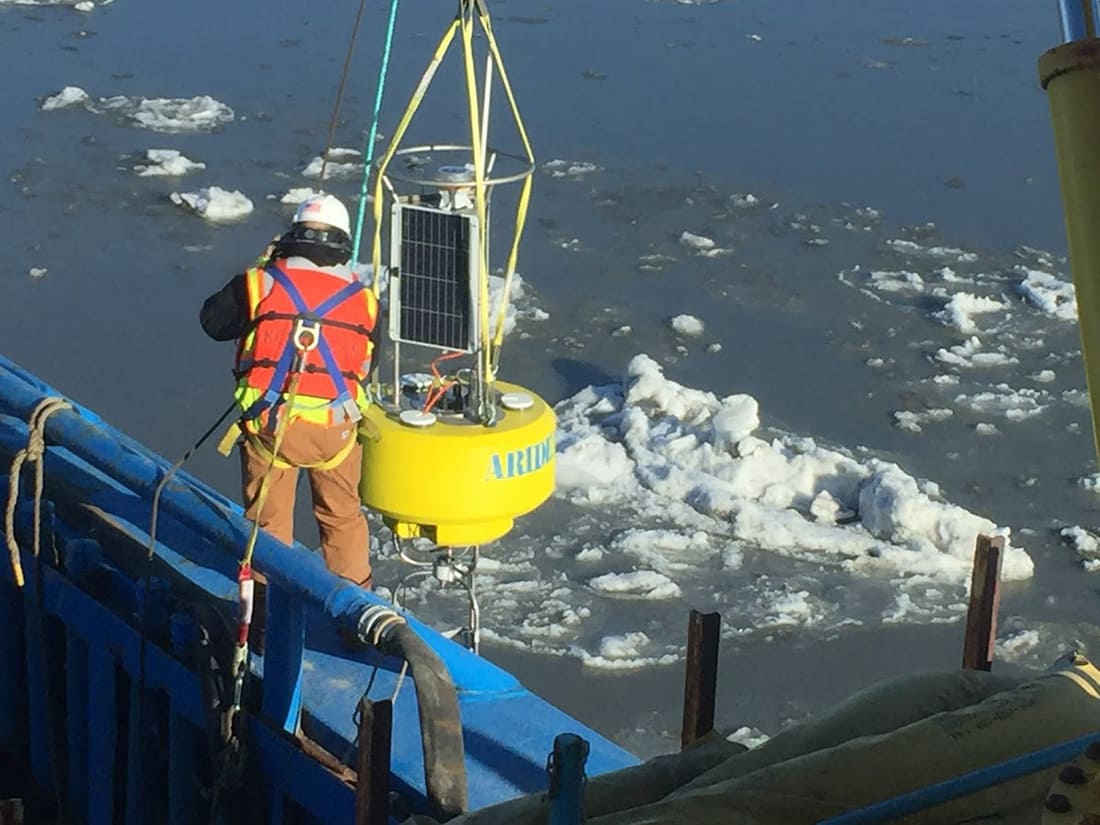
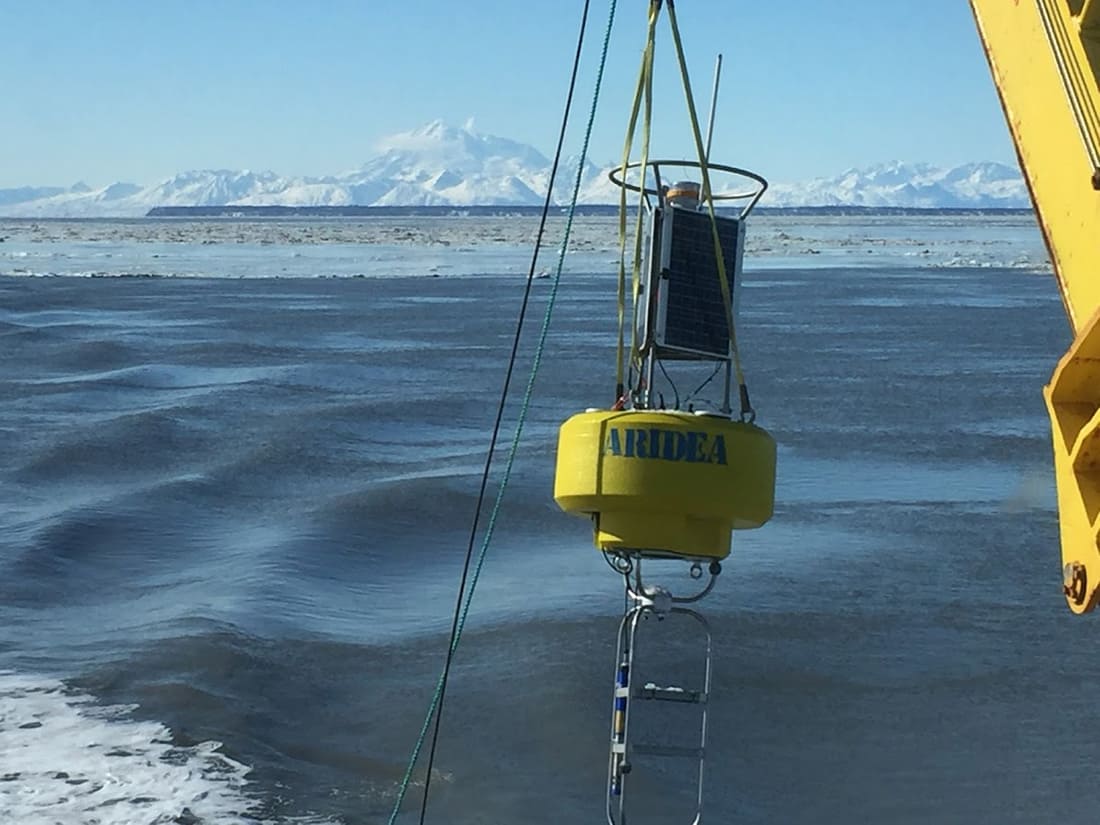


Technicians installing Aridea’s buoy in the water
The buoy system was deployed several times to monitor and report on environmental conditions until the weather conditions allowed divers to permanently repair the leak. The buoy system designed and integrated by Aridea proved to be a key tool in providing crucial data in analyzing the environmental impacts of the leak until these repairs were completed.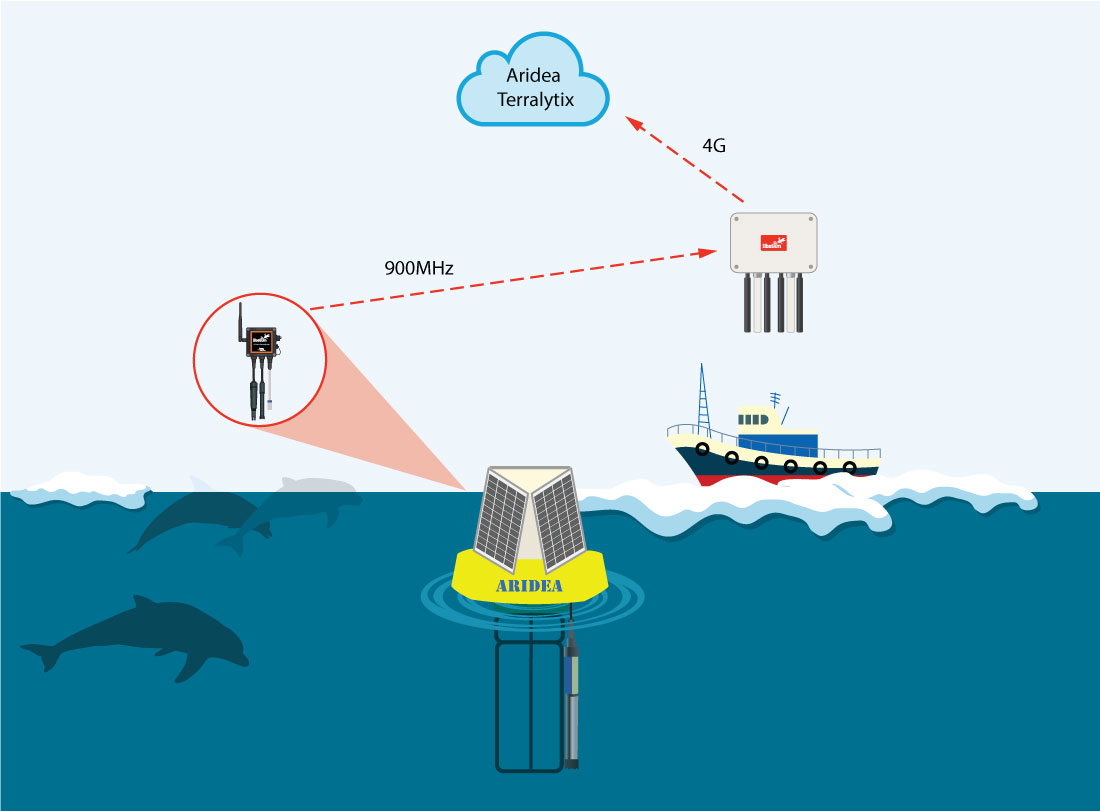
Diagram of Aridea’s solution at Cook Inlet (Alaska)
Once on-site, the buoy deployment was challenged by ice coverage and movements due to the extreme temperatures and tidal changes in the area. The buoy and sensors chosen for the deployment were designed to withstand these extreme conditions. Due to coast guard restrictions placed around the leak site, the buoy had to be able to drift through the affected area by timing the tidal cycles in the area. The buoy was deployed by a crane mounted on the ship. Once the buoy was set adrift in the affected leak area, the ship was at times 1-2 miles away from the buoy. However, buoy communication was maintained due to the flexibility of the on-board Waspmote’s long-range 900Mhz capability.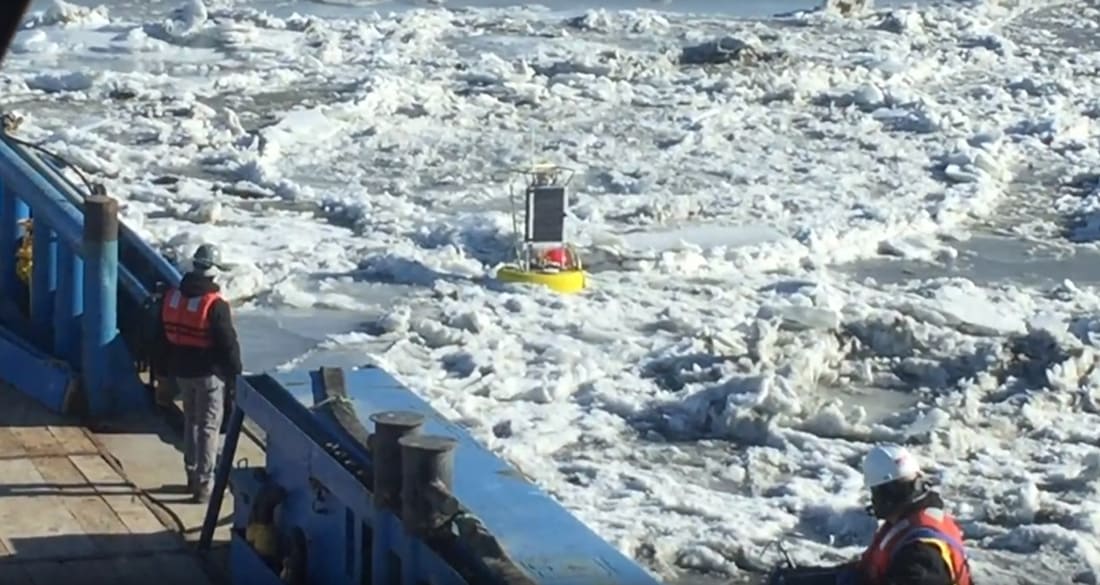
Aridea’s sensor buoy operating in the frozen waters of Cook Inlet
Aridea’s Director of Engineering Rob Moore stated, “One key attribute in our success to meet this aggressive timeline and challenging environmental conditions was our choice of hardware vendors. Aridea’s choice to use Libelium’s Waspmote platform allowed for rapid and flexible integration of sensors from multiple vendors”.This case study helps to achieve the following Sustainable Development Goals:
More info:
References:
Want to receive this and more IoT news directly to your email?
🔔 Subscribe to our newsletter and don’t miss anything! You will learn about IoT and how it helps to make the world a more sustainable and efficient place.
sign me in!Stay up to date in IoT!
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest, exciting news.
More than 18 years of experience in IoT support us.


















IoT Solutions for
IoT Products
© Libelium Comunicaciones Distribuidas S.L. | Terms And Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookies Policy | Security Policy | Reporting Channel